Dental X-Ray
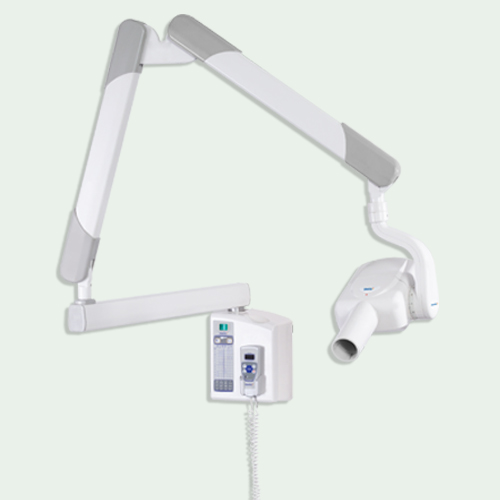
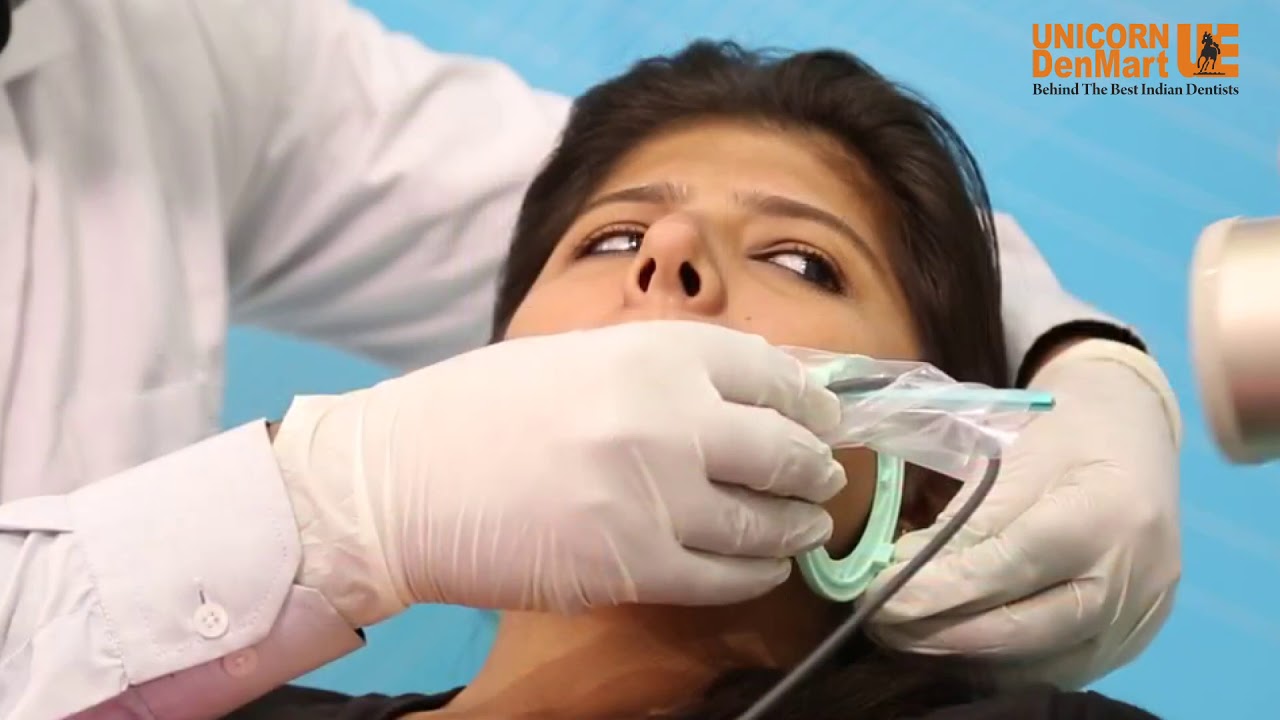
The use of a dental X-Ray machine allows a dentist to better diagnose and plan treatment operations by providing a clear view of the internal radiolucent areas. Detecting and treating dental disorders that can save money for the patient.
Dental X-Ray equipment is a type of electromagnetic energy that can either flow through or be absorbed by solid materials. Dental X-Rays are ionising radiation with enough energy to ionise atoms and disrupt the connection between molecules.
Due to the quick drop in the rate of swiftly moving electron speed, Dental X-Ray Portable Machine are emitted when they collide and interfere with the target anode. In this process, 99 percent of the heat is generated and less than 1% of the Dental X-Ray Unit is produced. When high-speed electrons lose energy in an X-Ray tube’s target.
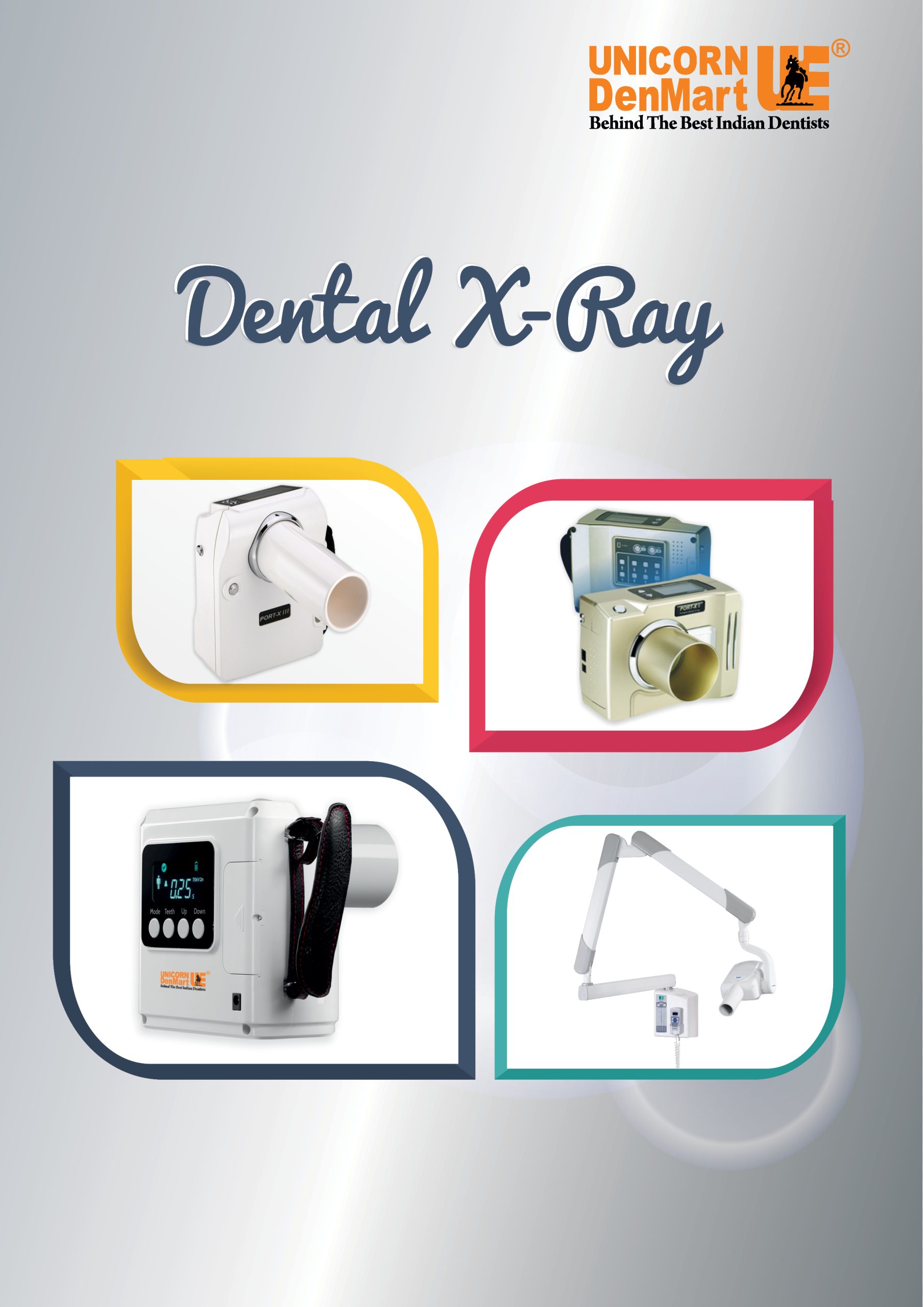
Types of Dental X-Rays:
Extraoral
Intraoral
Panoramic X-Ray: It records the whole image of the mouth at once, which aids in the detection of any impacted teeth, as well as the identification and treatment of tumours.
Tomograms: It depicts slices of the mouth so that any difficult-to-see structures can be identified.
Computed Tomography: In dentistry, it’s commonly utilised to detect bone fractures or tumour growth. It also aids in implant placement by determining the density of the bone.
Periapical: It is utilised to detect any abnormalities in the tooth’s root structure and periapical areas, such as bone health, periodontal ligament, and interproximal areas.
Bitewing: To determine the cast repair and marginal integrity of the fillings, as well as to detect gum disease.
Occlusal: To detect full tooth development along the mouth’s arch.
Recent Blog
Piezoelectric Surgery Devices: The Next Wave in Dental Surgeries
Embracing Innovation in Dentistry: The Rise of Piezoelectric Surgery...
Read MoreUnveiling a New Dimension in Dental Care: The Era of Dental CBCT Machines
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern dentistry, the introduction...
Read MoreThe Rise of Portable Dental X-Ray Units: Convenience Meets Technology
In recent years, the dental industry has witnessed a significant...
Read MoreHow Digital Imaging is Revolutionizing Dental Diagnostics
In the annals of dental history, diagnostics have always been...
Read More